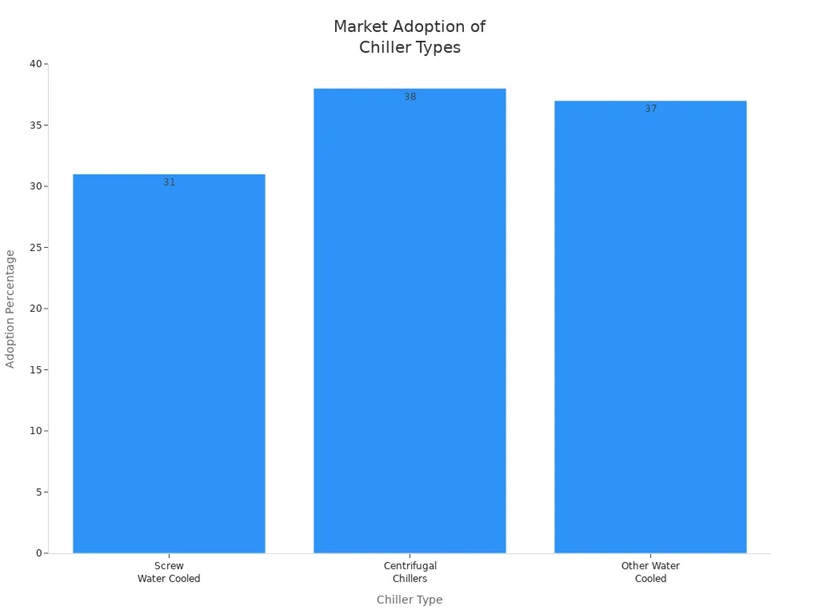
You need a strong cooling system for big buildings. Water cooled screw chillers work very well for this job. These chillers cool large spaces and save energy. They also run quietly. Your building stays comfortable all the time. Water cooled chillers help your building for many years. Many buildings pick water cooled screw chillers because they work well. They are also very reliable. About 31% of big buildings use water cooled screw chillers.
|
Chiller Type
|
Market Adoption Percentage
|
|
Screw Water Cooled Chillers
|
31%
|
|
Centrifugal Chillers
|
38%
|
|
Other Water Cooled Chillers
|
37% (overall commercial sector)
|
Water cooled screw chillers fit many building needs. They help solve cooling problems in busy places. These chillers last a long time. They save energy and keep your building working well.
Key Takeaways
-
Water cooled screw chillers work very well. They give strong cooling to big buildings and save energy.
-
These chillers make little noise. This is good for places where noise matters.
-
Cleaning condenser tubes often keeps them working well. It also helps avoid expensive repairs.
-
Water cooled chillers can be used in many places. They work in hospitals, data centers, and factories.
-
Picking water cooled screw chillers can lower energy bills. It also helps protect the environment.
Water Cooled Screw Chiller vs. Other Chillers
Air Cooled vs. Water Cooled Screw Chillers
You want your building to feel cool and nice. Air cooled chillers and water cooled chillers both help with cooling. They work in different ways. Water cooled chillers use water to take away heat. Air cooled chillers use air instead. This changes how well each chiller works, especially in big buildings.
|
Chiller Type
|
Efficiency Rating
|
Key Factors Affecting Efficiency
|
|
Water-Cooled Chillers
|
Higher
|
Work at lower temperatures, not much affected by outside weather
|
|
Air-Cooled Chillers
|
Lower
|
Have hotter condenser temperatures, more affected by outside weather
|
Water cooled chillers are more efficient. They work better in large spaces. They do not need outside air temperature to work well. You get steady cooling, even when it is hot outside. Water cooled chillers also have higher minimum COP values. For example, a water cooled screw chiller with over 1163KW capacity has a minimum COP of 4.60. Air cooled chillers with similar size have a minimum COP of 2.80.
Screw Compressors vs. Centrifugal Compressors
You may wonder how screw and centrifugal chillers are different. Screw chillers use twin-rotor compression. This gives you many choices for cooling power. They work from 10% to 100% of their load. Centrifugal chillers start at about 200 tons and can go much higher. They use inlet vanes to change their cooling power. Screw chillers cost less to maintain and are good for mid-sized buildings.
|
Compressor Type
|
Reliability Factors
|
|
Centrifugal Compressors
|
Fewer moving parts and less wear make them reliable for long use.
|
|
Screw Compressors
|
Need more maintenance if started and stopped often or used in tough places.
|
Screw chillers are easier to take care of than centrifugal chillers. You spend less time and money fixing them.
Large-Scale Applications
You find water cooled screw chillers in many big buildings. Hospitals, data centers, and factories use these chillers. They need strong and steady cooling. Water cooled screw chillers can cool from 121 kW to over 3500 kW. This makes them great for places that need lots of cooling.
Tip: If you run a big building, water cooled screw chillers are a good choice. They give you strong cooling, save energy, and work well for a long time.
Key Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers

High Cooling Capacity
Big buildings need chillers that can cool large areas. Water-cooled chillers cool better than most other types. These chillers use water to move heat away fast. Water works faster than air for cooling. This makes them good for places with many people or machines. Water-cooled screw chillers come in many sizes. They can cool from 78 to 500 tons, or 273 to 1,756 kW. You can choose the size that fits your building.
|
Cooling Capacity (Tons)
|
Cooling Capacity (kW)
|
|
78 to 500
|
273 to 1,756
|
Water-cooled chillers keep your building cool, even in hot weather. You get steady cooling all year long. This is important for hospitals, data centers, and factories. These chillers are good for tall buildings. They do not need big outdoor units. You get strong cooling without using too much space.
Tip: Pick water-cooled screw chillers if you want strong and steady cooling.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
You want to save money and use less energy. Water-cooled chillers help you do both. These chillers use water, which moves heat better than air. This means they use less energy to cool your building. You get lower energy bills and save money.
Water-cooled chillers have higher energy efficiency ratios than air-cooled chillers. They last longer because they run at lower temperatures. This means less damage to the parts. You spend less on fixing or replacing them. These chillers use closed-loop systems that recycle water. This helps save water and lowers your water bills.
Here is how much you can save each year with a high efficiency water-cooled chiller:
|
Chiller Type
|
Annual Energy Cost ($/yr)
|
Lifetime Energy Cost Savings
|
|
High Efficiency Model
|
$30,012
|
$162,957
|
|
Required Efficiency Model
|
$32,330
|
$128,037
|
|
Lower Efficiency Model
|
$40,828
|
N/A
|
You see real savings on your energy bills. You also help the planet by using less energy and water. Water-cooled chillers are good for the environment. They use less energy, last longer, and need less fixing. This gives you good value for many years.
Quiet and Reliable Operation
You want your building to be quiet and comfortable. Water-cooled chillers make less noise than air-cooled chillers. They do not use big fans, so they are quieter. Small water-cooled chillers make about 60 to 70 decibels of noise at one meter. Big industrial chillers make 70 to 90 decibels. This is quieter than many other cooling systems.
|
Type of Chiller
|
Noise Level (dB)
|
Distance from Chiller
|
|
Smaller Water Cooled Scroll Chiller
|
60 - 70
|
1 meter
|
|
Larger Industrial Water Chiller
|
70 - 90
|
1 meter
|
Water-cooled chillers are also very reliable. They work well even when it is hot outside. You do not have to worry about them breaking down. These chillers need less fixing because water is cleaner than air. This means fewer repairs and lower costs for you.
Note: Water-cooled screw chillers give you quiet, strong, and lasting cooling. You get a system that works well for many years.
Performance in High-Demand Settings
Consistent Cooling
It is important to keep your building cool all the time. Water cooled screw chillers work well when things get busy. These chillers use special compressors and smart controls. You always get water at the right temperature. It does not matter how much cooling you need.
Here is how water cooled screw chillers keep cooling steady:
|
Feature
|
Description
|
|
High-efficiency compressor
|
Keeps cooling strong with less energy, so you save money.
|
|
Optimized control systems
|
Changes cooling power as needed, so you do not waste energy.
|
|
Operational flexibility
|
One chiller can cool many things, even when demand is high.
|
You can count on these chillers for air conditioning and other needs. The system changes quickly when you need more or less cooling. You do not have to worry about sudden temperature drops or wasted energy. Water cooled screw chillers keep your building safe and comfortable.
Durability and Longevity
You want your cooling system to last a long time. Water cooled screw chillers can work for many years. Most chillers last from 15 to 25 years. Some chillers last even longer if you take good care of them. Doing regular checks helps your chiller last longer.
-
Water-cooled chillers usually last 15 to 20 years.
-
Most water cooled screw chillers last 15 to 25 years.
-
Some chillers can last over 25 years if cared for well.
-
If you do not take care of your chiller, it may last only 10 years or less.
Water cooled chillers do not break down as easily as air-cooled chillers. Chilled water helps protect the equipment. You spend less time fixing your chiller. Clean water and regular checks help your system work smoothly.
Precise Heat Transfer
You need good heat transfer for strong cooling. Water cooled screw chillers use new technology to move heat fast. Chilled water takes heat from your building and sends it away.
|
Technology
|
Description
|
|
High-efficiency seamless copper tubes
|
These tubes have special fins inside to help move heat better.
|
|
Shell and tube condenser
|
Copper tubes have extra surface to help exchange heat faster.
|
|
Shell and tube evaporator
|
Uses a plate to help water flow and move heat, with insulation to keep temperatures steady.
|
Good heat transfer helps your chiller work its best. You use less energy and save money. Things like water flow, refrigerant, and clean pipes help your chiller work well. Dirt and scale can make your chiller less efficient. Keeping your system clean helps you get the best cooling.
Water cooled screw chillers use chilled water to move heat well. You get steady cooling, lower bills, and reliable performance. These chillers help you cool big spaces without wasting energy.
Tip: Clean pipes and regular checks help your chiller give you the best cooling and chilled water.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
System Design and Space Needs
When you plan water cooled chiller systems, think about your building’s setup. These systems need a cooling tower, pumps, and pipes. You must have enough room for all the parts. Water cooled chiller systems work best in medium or big buildings. They give steady cooling and save energy. You may pay more to install them because they need extra equipment. The table below shows how design can change how well the system works:
|
Aspect
|
Impact on Performance
|
|
Efficiency
|
Changes how much energy and money you use.
|
|
Installation Costs
|
Higher for water cooled chillers because of extra parts.
|
|
Maintenance Requirements
|
Regular care is needed to keep the system working well.
|
|
Operational Effectiveness
|
More steady cooling in bigger buildings than air cooled chillers.
|
Water cooled chiller systems use supply temperatures from 38 to 44 degrees Fahrenheit. This helps keep your building cool and saves energy. If you use higher delta Ts with lower supply temperatures, you might use more energy.
Maintenance Requirements
You want your water cooled chiller systems to last many years. Regular care helps your system work its best. Clean condenser tubes once a year. Check refrigerant and oil levels often. Watch water flow to stop problems. Clean and check condenser tubes with chemicals or brushes to keep things running well. These steps help you spend less on repairs and avoid big problems.
-
Clean condenser tubes every year.
-
Check refrigerant and oil levels often.
-
Watch water flow to stop issues.
Tip: Regular care keeps your water cooled chiller systems working well and saves you money.
Integration with Building Systems
Modern water cooled chiller systems connect easily to building automation. You can change cooling settings for comfort and saving energy. Many systems use H-LINK wiring for easy control. Some models, like the WVY series, have a 7-inch touch screen for direct control. You get flexible control and can change cooling for what you need. This helps you save energy and keep your building comfy.
-
Water cooled chiller systems work with automation for easy control.
-
You can change cooling for different rooms.
-
Central control makes things simple.
Note: When you pick water cooled chiller systems, you get steady cooling, easy care, and smart control for your building.
Real-World Uses for Water Cooled Screw Chillers
Commercial Buildings
Water cooled screw chillers are used in many businesses. They help offices, malls, and hotels stay cool. These chillers work well even when lots of people are inside. Many businesses pick these chillers because they save energy and last a long time.
-
The AquaEdge™ 23XRV chiller cools large spaces and has a SEER over 10.0. It saves energy and does not take up much space.
-
Some buildings use two chillers. One is always ready if the other needs fixing.
-
Chilled water moves through chilled beams, air handlers, and fan coils. This keeps every room comfortable.
-
Some chiller plants have extra cooling towers and special loops. This means no single part can stop the whole system from working.
-
Daikin Screw Inverter units change speed to save energy and help pumps work better.
These cooling systems give you comfort, flexibility, and strength. They help many businesses and save money.
Industrial Facilities
Factories and plants need chillers they can trust. Water cooled screw chillers keep machines and workers safe. They handle lots of heat from big machines. You get steady cooling for work areas and storage rooms.
-
Industrial chillers help with process cooling and climate control.
-
You see chillers where products must stay at the right temperature.
-
These chillers help stop shutdowns and keep everything running.
People pick these chillers because they are strong and last long. They help your factory work well and protect your money.
Healthcare and Data Centers
Hospitals and data centers need very careful cooling. Water cooled screw chillers keep important equipment safe. They keep patient rooms, labs, and server racks at the right temperature.
-
Hospitals use chillers for operating rooms and patient care.
-
Data centers need chillers to stop computers from getting too hot.
-
These chillers are quiet and always keep things cool, which is very important.
You can count on these chillers for safe and steady cooling. They help you follow rules and keep your building working right.
You want a cooling system that works well and saves money. Water cooled screw chillers have high power and use energy wisely. They are also very reliable. You can put them in many places, like hospitals, factories, and data centers.
-
These chillers use water to move heat better. This helps you use less energy and make less pollution.
-
You can follow tough energy rules and help the planet.
-
New designs make these chillers quieter, smaller, and simple to take care of.
Choosing water cooled screw chillers for your building is a smart choice.










